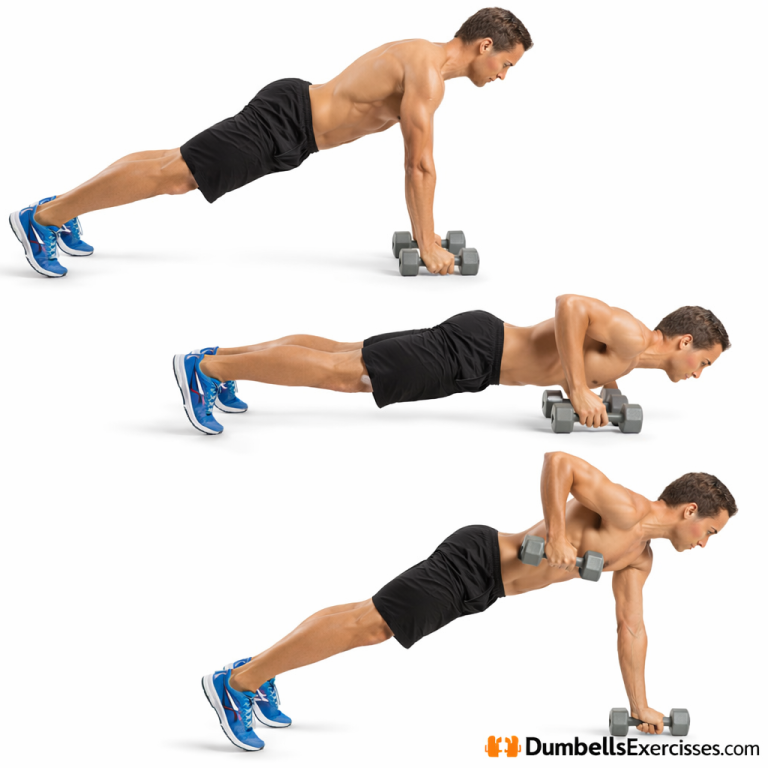
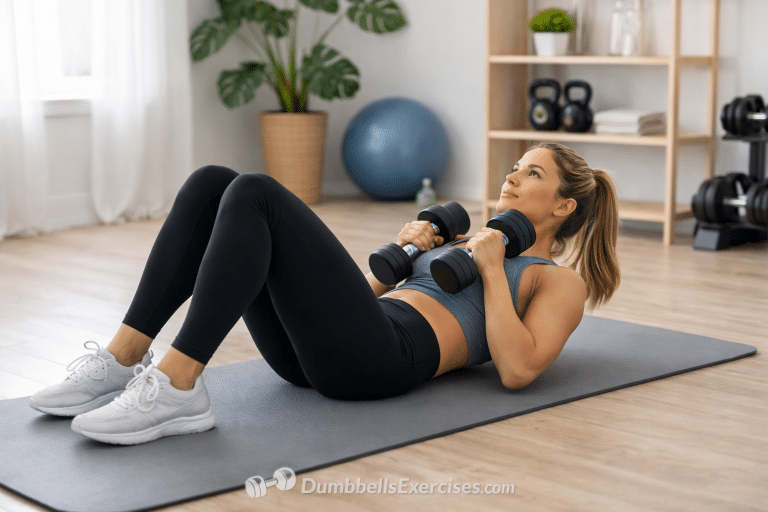
1. Foundational Strength for Long-Term Development
Grip strength training begins with a focus on building durable tendons, balanced muscle activation, and proper wrist alignment. A strong foundation helps the hands adapt to heavier loads while reducing stress on the joints. Slow, controlled movements encourage safe progression and allow the body to develop the structural integrity required for advanced work. This stage prepares the entire lower arm for long-term results.
The early foundation phase should emphasize precision and patience rather than intensity. Light repetitions with attention to form strengthen neuromuscular pathways and improve fine motor control. As consistency builds, individuals notice increased confidence when handling daily tasks or performing exercises involving the hands. Establishing these fundamentals prevents plateaus and contributes to healthier, stronger movement patterns.
2. Crushing Exercises for Practical Hand Power
Grip strength training also benefits from crushing exercises that challenge the entire hand to exert firm, sustained pressure. These movements include grippers, towel squeezes, and thick-handled implements that create substantial forearm recruitment. Crushing drills help strengthen the small muscles that stabilize the hand during real-world tasks. Athletes who include these exercises gain measurable improvements in everyday strength.
Crushing exercises should be performed with moderate frequency to prevent overuse and ensure consistent progress. Gradual increases in tension or tool thickness provide challenge without excessive strain. These drills help develop control during long-duration activities such as carrying weights or performing manual labor. Over time, crushing strength produces noticeable improvements in both everyday tasks and athletic situations.
3. Pinch Training for Thumb and Finger Control
Grip strength training expands further with pinch exercises that target the thumb and fingertips through lateral pressure. Movements such as plate pinches, block holds, and pinch carries teach the hand to maintain control without relying on the palms. This type of training develops finger independence and enhances coordination under load. The thumb in particular becomes significantly stronger through repeated pinching practice.
Pinch training should be approached gradually because the small joints of the fingers fatigue quickly. Varying the thickness and texture of the objects used can keep training stimulating and reduce repetitive stress. Short bursts of effort help build resilience while maintaining technique. As control improves, the individual develops a higher degree of dexterity and fine-motor precision.
4. Support Holds for Greater Endurance
Grip strength training becomes even more effective when support holds are incorporated to improve time-under-tension strength. Exercises such as farmer’s carries, dead hangs, and suitcase walks challenge the hands to maintain contact with an object for extended periods. These drills significantly enhance grip endurance and improve the stability of the shoulders and core. Longer holds help develop the capacity required for functional strength tasks.
Support holds should focus on duration before intensity to ensure safe progression. Moderate loads allow individuals to maintain proper posture and joint alignment. Over time, adding distance or time provides measurable improvements in endurance. Support-style drills also help identify weak points that can be addressed in subsequent training phases.
5. Wrist and Forearm Conditioning for Stability
Grip strength training also relies on strengthening the wrists and forearms to support greater hand performance. Conditioning movements such as wrist curls, reverse curls, pronation, supination, and rotational drills develop a stronger base for gripping actions. These exercises help distribute force evenly across the lower arm, reducing strain during heavy or repetitive tasks. Improved joint stability enhances control and reduces discomfort during gripping movements.
This form of conditioning requires attention to detail because balanced development is essential for optimal performance. Training the forearm from multiple angles helps prevent muscular imbalances and supports long-term joint health. Slow, deliberate repetitions encourage proper technique and provide safer strength gains. Consistent practice builds durability and smoother motion patterns during all forms of lifting and carrying.
6. Implement Variety for Enhanced Adaptability
Grip strength training benefits greatly from specialized implements that challenge the hands in new ways. Thick bars, sandbags, ropes, climbing holds, and adjustable tools all introduce irregular shapes and shifting loads that encourage broader muscle recruitment. These implements stimulate high neural activation, increasing the responsiveness of the hands under stress. Athletes often experience faster improvements when exposed to unconventional resistance.
Training with various implements helps develop adaptability, which is essential for functional performance. The constantly changing nature of certain tools enhances coordination and teaches the hands to adjust rapidly to different forces. Implement work adds variety that keeps training engaging and reduces plateaus. This form of stimulation strengthens areas that traditional exercises may not reach.
7. Integrated Strength Work for Total Performance
Grip strength training reaches its highest effectiveness when integrated with full-body movements that require coordinated effort. Exercises such as rope climbs, kettlebell carries, pull-up variations, and heavy farmer’s walks all emphasize grip while engaging multiple muscle groups. This integrated approach builds strength that extends beyond isolated hand work. Athletes develop improved control, stability, and functional power through these compound tasks.
Integrated movements should be added after building a solid base to ensure safety and avoid premature fatigue. Using moderate loads at first allows the hands to adapt to coordinating with larger muscle groups. With consistency, individuals notice increased endurance during complex movements. This advanced approach enhances overall athleticism and creates a more unified strength system.